The information contained herein was prepared between mid-September and October 2024.
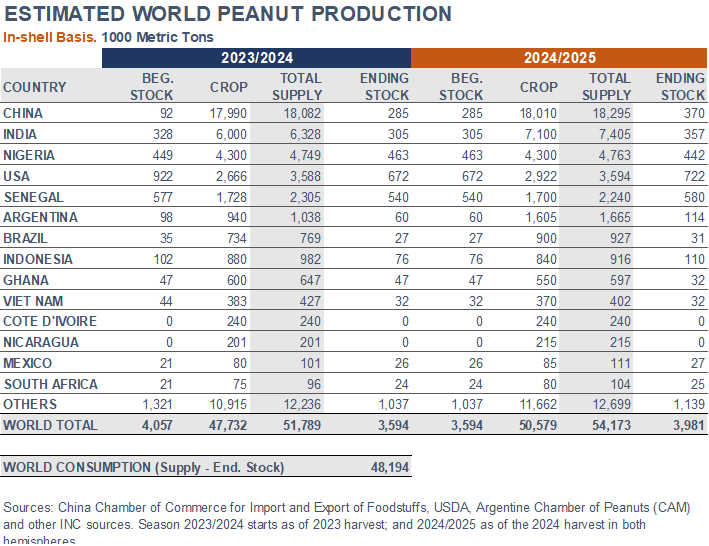
China. According to the Chinese Chamber of Commerce, planted area saw an increase in 2024 compared to last year, primarily driven by declining prices of competing crops, especially corn. Planting grew by approximately 10%, with larger expansions in the major producing provinces of Henan and Jilin.
Weather conditions throughout the growing regions have been challenging, particularly in Henan province and in western Shandong province, where, early in the sowing season, excessive heat and drought hampered growth, followed by heavy rainfall, which led to root issues and adversely affected yield per land area. Nonetheless, overall production was expected to remain high due to the increased planting area.
As the new peanut harvest season has progressed, major producing areas like Henan and Shandong have begun listing their peanuts, with northeastern provinces expected to follow as of October. The opening prices for the edible grade were set at approximately US$1,270 per metric ton, while oil peanuts were priced at around US$1,130 per MT. However, the abundant supply and weak downstream demand have contributed to a decline in both peanut futures and spot prices. Lower prices benefit the export of high-quality edible peanuts. In contrast, countries aiming to export oil peanuts to China need to remain competitive in the Chinese market.
USA. As per the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) October 2024 Crop Production Report, Hurricane Helene, which made landfall in late September 2024, affected several agricultural regions, including peanut-growing areas in Alabama, Georgia, and the Carolinas. However, the full impact of the storm might not be reflected until future reports.
Peanut production for 2024 showed an overall increase in both planted and harvested areas compared to the previous year. Total peanut planted area reached 1.81 million acres (732,300 hectares), up 10% from 2023. Similarly, the area harvested grew by 12% to 1.75 M acres (708,400 ha). Georgia, the largest peanut-producing state, reported an expansion of 10% in its harvested acreage, estimated at 845,000 acres (342,100 ha). Texas, with 210,000 acres (85,000 ha), saw an increase of 27%. Alabama’s area rose 9%, to 186,000 acres (75,300 ha), while Florida’s expanded 6%, to 161,000 acres (65,200 ha).
Yield was forecasted at 3,683 pounds per acre (4.12 MT/ha), 2% down from 2023. However, driven by the overall increased acreage, total production was expected to increase 10%, reaching 6.44 billion lbs. (2.92 M MT). Georgia’s crop was forecasted to reach 3.21 B lbs. (1.46 M MT), an increase of 2% from 2023. Alabama was expected to produce 614 M lbs. (278,400 MT), 30% higher than the previous year. Florida’s crop was projected 14% up, at 596 M lbs. (270,200 MT). Texas was also expected to see an increase, with production projected at 525 M lbs. (238,100 MT), up by 14% from last year.
Argentina. The Argentine Chamber of Commerce reported that 416,490 ha were planted for the 2023/24 season and 416,039 ha were harvested. Yield was estimated at 3.8 MT/ha on an in-shell basis (2.7 MT/ha kernel basis), resulting in a production of 1,604,722 MT on an in-shell basis (1,123,305 MT kernel basis), up by 71% from 2022/23. Exports were, at the time of this report, projected at 740,950 MT of shelled peanuts. Domestic demand, including blanching losses, milling and seed use, was anticipated to reach 344,695 MT.